Blepharoplasty
Eyelid Surgery
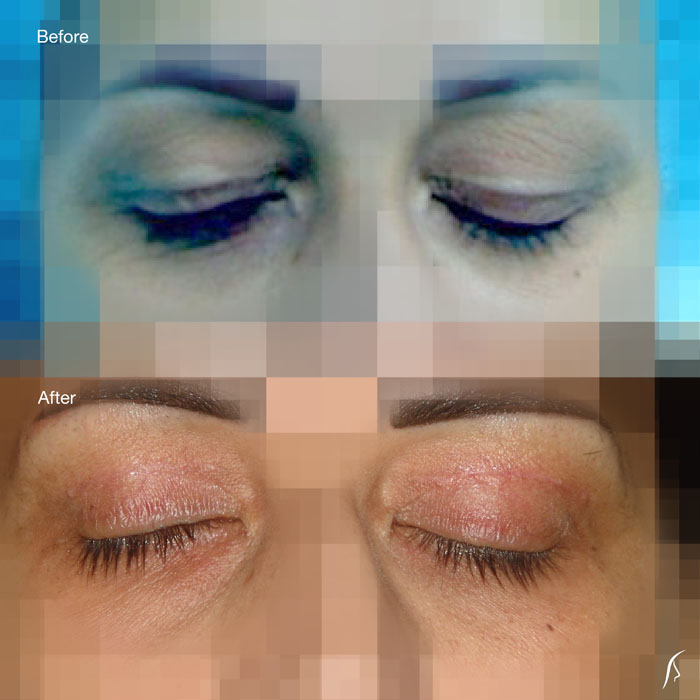
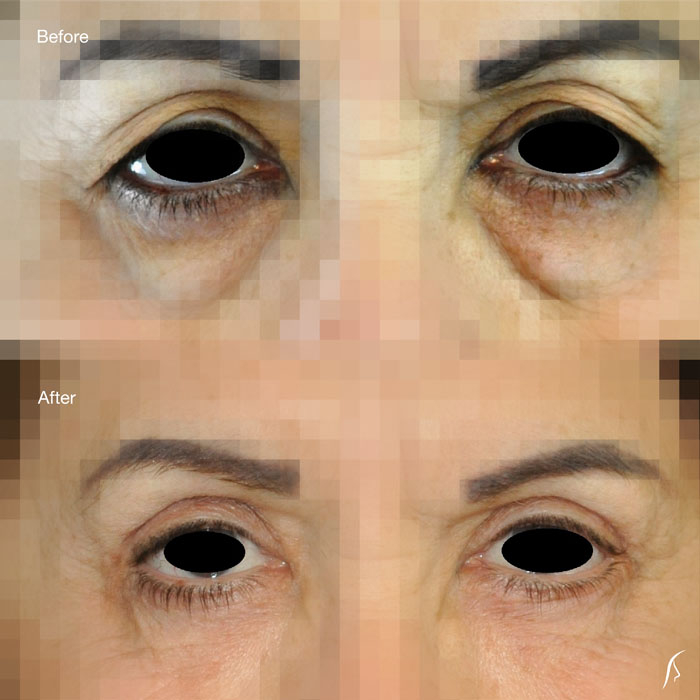
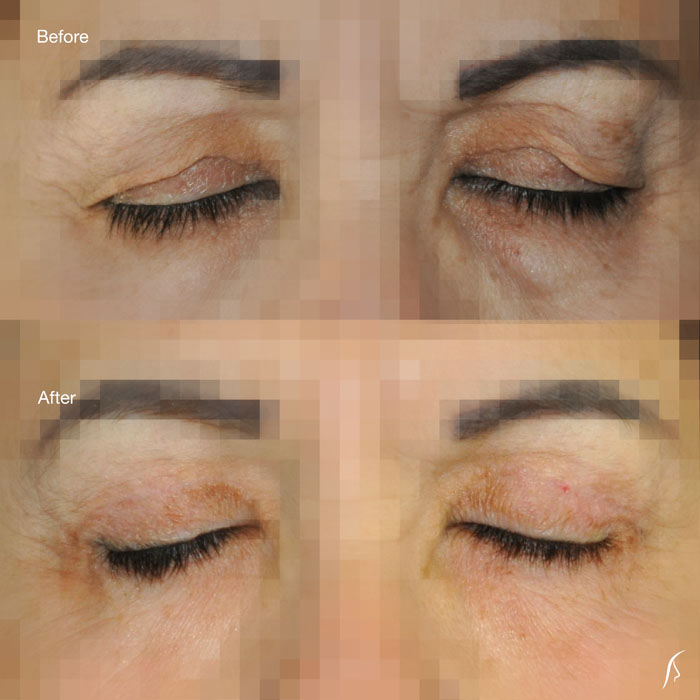
Upper eyelid droopiness can cause vision impairment by reducing your side vision (peripheral vision), especially the upper and outer parts of your visual field, make you look older and will make your eyes feel heavy. Upper blepharoplasty can correct these problems.
Lower eyelid cosmetic complaints are usually from the pseudohernation of periorbital fat, wrinkling of the lower orbital skin, orbicularis muscle hypertrophy or from exposure of the lower lid due to aging, resulting in eye dryness and other problems.
Anesthesia:
Medications are administered for your comfort during the surgical procedure. The choices include intravenous sedation with local infiltration (local anesthesia) or general anesthesia. Your doctor will recommend the best choice for you.
The surgery:
The upper eyelid can be corrected through an incision within the natural crease on the eyelid. This allows for removal or repositioning of fat deposits, tightening of muscles and removal of excess skin.
The lower eyelid may be corrected with an incision just below the lower lash line. Through this incision, excess skin in the lower eyelid is removed and the excess fat can be repositioned or removed. Lower canthopexy might be done to prevent ectropion in select patients.
An alternate technique which does not involve skin excision is the transconjunctival technique. Incisions are done on the inside of the lower eyelid and fat is then removed or redistributed.
A blepharoplasty operation usually requires 1–3 hours to complete. Post-operatively, the initial swelling and bruising consequent to the surgery will subside and resolve with 1–2 weeks. The final results of the operation will become apparent after several months.
Risks of eyelid surgery include:
Bleeding, dry eyes, infection, difficulty closing the eyes, injury to the eye muscles, infection, scarring and ectropion.